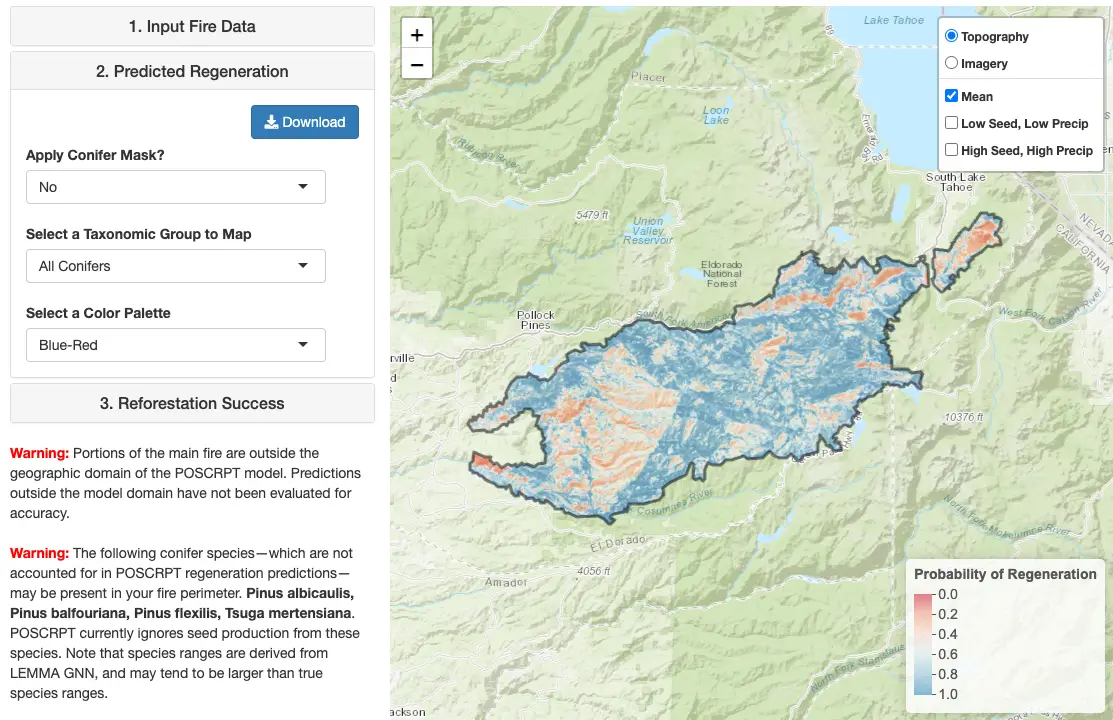
Postfire Conifer Reforestation Planning Tool
Current Interfaces
The preprocessed interface for PostCRPT allows users to simply select a fire to see mapped predictions and download spatial data. It includes maps of probability of conifer regeneration, burn severity, high-severity patch size, and vegetation type. It includes all fires with perimeters available in public databases that burned from 1991-2023 in California and Western Oregon. Uses the latest version of the conifer regeneration prediction model (0.2b), which was trained on a larger postfire regeneration dataset, uses updated environmental predictors, and has improved predictive accuracy compared to previous versions (see the "About" tab of the tool for details). Includes a simple and customizable postfire reforestation prioritization and planning module.The custom-input interface for PostCRPT allows users to make predictions within weeks after a fire by inputting fire-perimeter and burn-severity data. Input data can be obtained from RAVG, or created using Google Earth Engine. A sample dataset is also available in the about tab of the tool. Includes postfire seed-production and weather scenarios and taxon-specific predictions for fir and pine. Uses an older version of the conifer regeneration prediction model (0.123). Accounts for effects of seed production only from species included in the Stewart et al. 2021 dataset.
Overview
The Postfire Conifer Reforestation Planning Tool (PostCRPT) helps managers target reforestation resources to where they are most needed for postfire forest recovery.
PostCRPT predicts the probability of postfire conifer regeneration under varying postfire precipitation and seed production scenarios. Predictive models were fit using data from 1,533 plots, spanning 24 wildfires, each measured five years after wildfire. PostCRPT predicts the probability that regeneration will occur within 60-m2 plots across wildfire footprints. Refer to Stewart et al. (2021) for details.
Presentations and Briefs
Accuracy
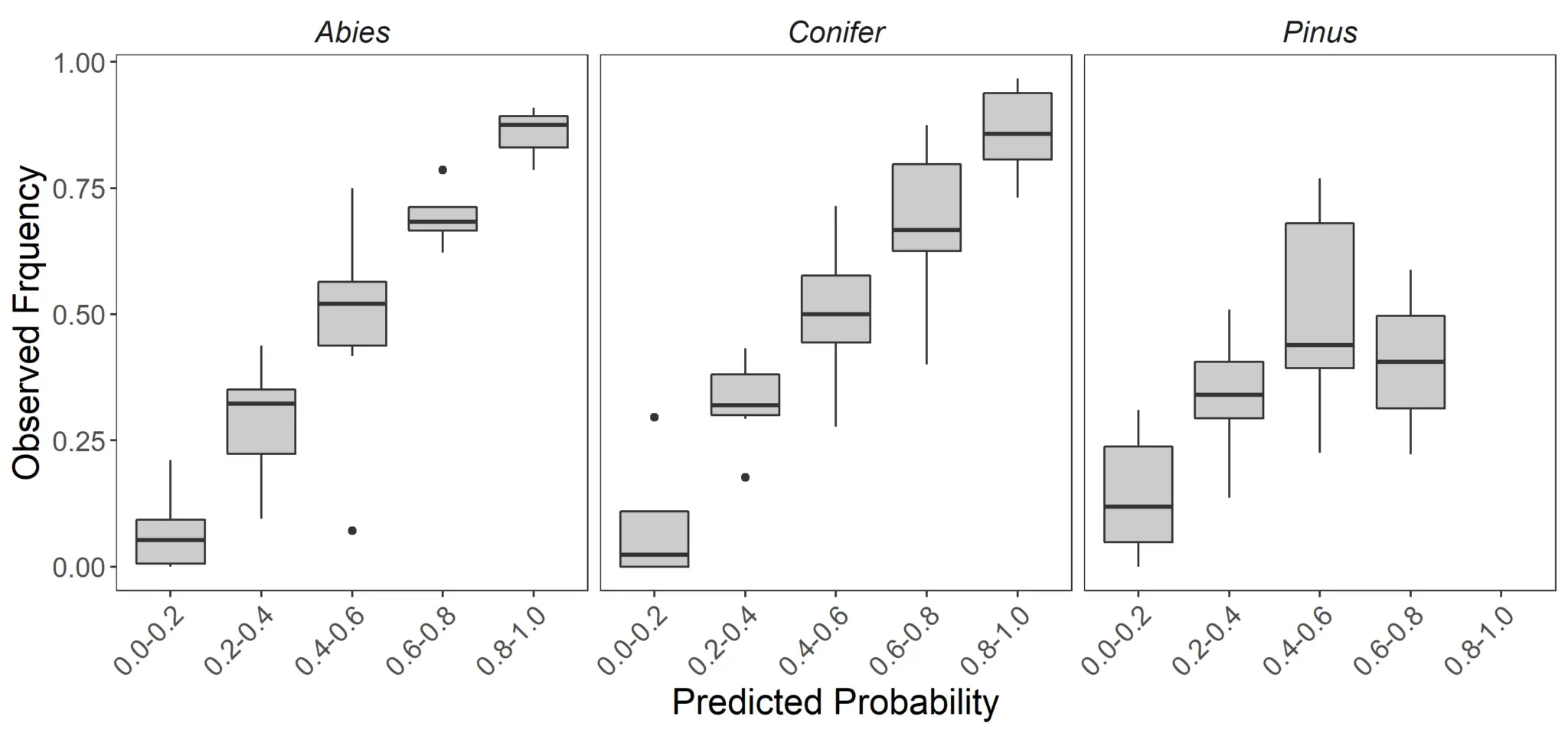
Prediction intervals for the PostCRPT statistical models are visualized using reliability diagrams (below). The reliability diagrams depict the performance of PostCRPT predictions when applied to new data, and were created using leave-one-fire-out cross-validation. Predictive performance is high in the all-Conifer and fir (Abies) models. The pine (Pinus) model has much room for improvement. See Stewart et al. (2021) for a full discussion.
Statistical Models
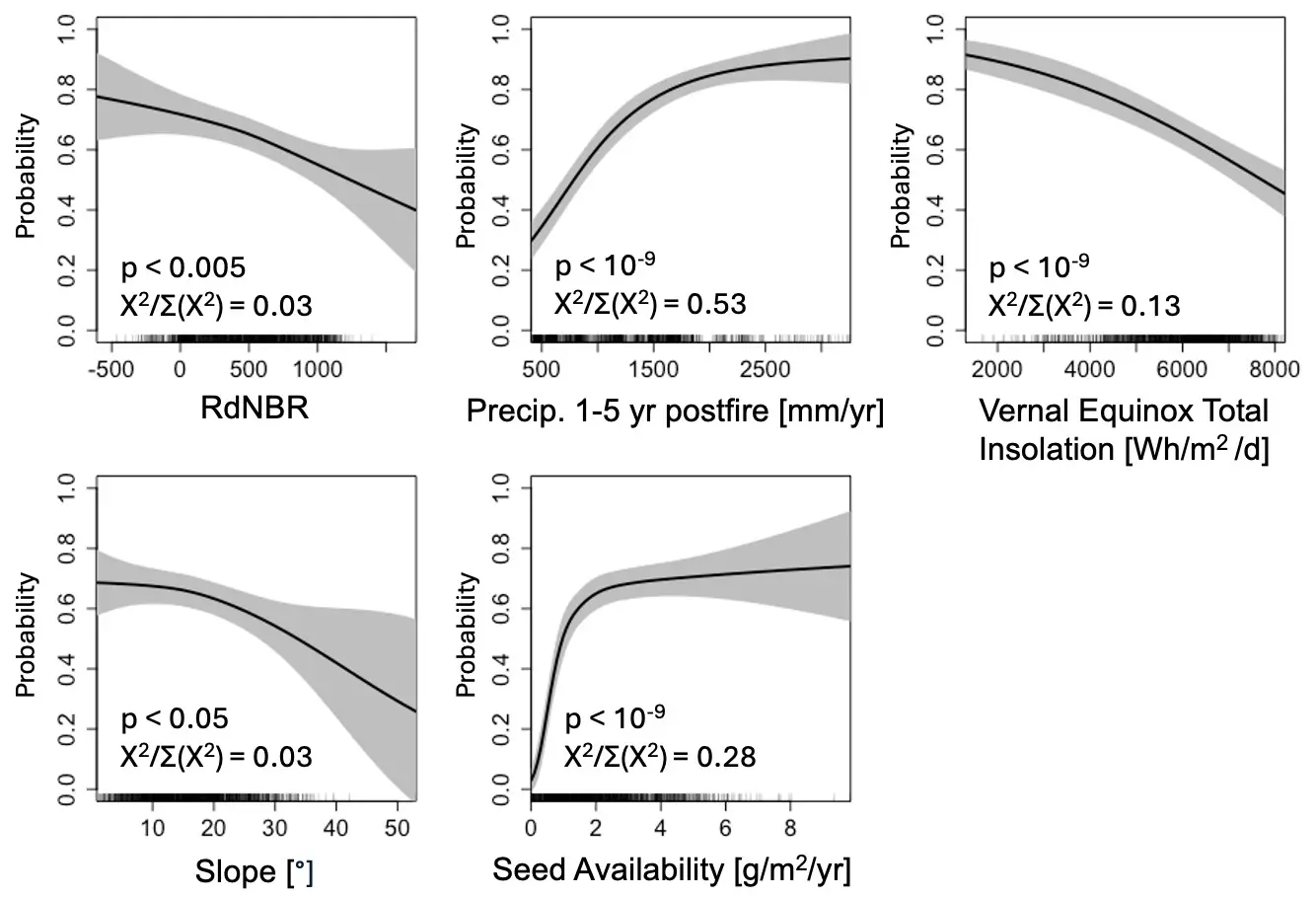
Seeking to follow the principle of Ockham’s razor, PostCRPT uses a lean set of predictor variables to avoid overfitting. Other candidate variables either did not improve out-of-sample model performance or appeared to result in overfitting.
Prioritization
PostCRPT includes a simple and customizable module for postfire planning and prioritization, loosely based on methods from Coppoletta et al. (2022). The module uses probability of natural conifer regeneration, high severity fire patch size, and vegetation type to suggest reforestation priority categories. The module is available in preprocessed interfaces for PostCRPT.

Citation
PostCRPT is a user interface for models developed by:
PostCRPT was adapted for the web from the poscrptR package, developed in a collaboration between the US Geological Survey Western Ecological Research Center and the US Forest Service:
The models developed by Stewart et al. (2021) build on an earlier spatial model developed by Shive et al. (2018), analyses of sensitivity to postfire climate presented by Young et al. (2019), and an earlier field-based model developed by Welch (2016).
Version History
PostCRPT Preprocessed Interface - Allows users to simply select a fire to see mapped predictions and download spatial data. Includes maps of probability of conifer regeneration, burn severity, high-severity patch size, and vegetation type. Uses the latest version of the conifer regeneration prediction model (0.2b), which was trained on a larger postfire regeneration dataset, uses updated environmental predictors, and has improved predictive accuracy compared to previous versions (see the “About” tab of the tool for details). Includes a simple and customizable module for postfire reforestation prioritization and planning.
-
PostCRPT version 0.232 – Released February, 2025. Adds integration with the Climate-Adapted Seed Tool (CAST). Once you’ve selected a fire, clicking on a map produces a link to find seed sources for that location.
-
PostCRPT version 0.231 – Released January, 2025. Fixes an issue in version 0.23 where burn severity was missing for fires that burned in 2015, and adds a raster attribute table for burn severity downloads.
-
PostCRPT version 0.23 – Released December, 2024. Includes all fires with perimeters available in public databases that burned from 1991-2023 in California and Western Oregon. Accounts for realized postfire weather and satellite imagery through 2024. Improvements to user interface. Added vegetation-type filtering to the postfire planning tab. Added LANDFIRE BpS group as a vegetation map option. Added version info and planning parameter metadata to downloads. Default parameters for the prioritization table were adjusted to emphasize areas with the greatest reforestation need. These default parameters are intended to reflect the current slow pace of reforestation on public lands and to highlight areas where reforestation is most urgently needed. If sufficient resources are allocated, reforestation of lower priority areas can still yield benefits that outweigh costs.
-
PostCRPT version 0.22 – Released March, 2024. Includes a preliminary interface for postfire reforestation prioritization and planning, loosely based on methods from Coppoletta et al. (2022). Does not yet account for vegetation type in reforestation prioritization and planning tab; for the time being please see Coppoletta et al. (2022) for vegetation-type filtering methods.
-
PostCRPT version 0.2 – Released December, 2023. We’re working on updates to the underlying statistical models (including an expanded postfire-regen dataset) and batch processed PostCRPT predictions for all fires. This interface displays progress toward these objectives. The current coverage includes all fires that burned from 2017-2021 in California and from 2017-2020 in Western Oregon. Unlike version 0.123, this version accounts for seed availability estimates from all conifer species mapped in CA and OR, not just the ones that are represented in the Stewart et al. (2021) dataset. Does not yet include taxon specific models for firs and pines (for the time being please see PostCRPT version 0.123 for taxon specific models).
PostCRPT Custom-Input Interface - Allows users to make predictions within weeks after a fire by uploading fire-perimeter and burn-severity data (e.g., from RAVG or created using Google Earth Engine). Includes postfire seed-production and weather scenarios and taxon-specific predictions for fir and pine. Uses older versions of the conifer regeneration prediction model. Accounts for effects of seed production only from species included in the Stewart et al. 2021 dataset.
- PostCRPT version 0.123 – Released January, 2022. Allows users to incorporate the effects of multiple sequential fires. Uses the 2020 version of LEMMA GNN forest structure maps. Updates the Stewart et al (2021) regeneration model to use 2020 version of GNN structure maps. Adds useful warnings. Expands geographic coverage. Refines the spatial domain.
-
PostCRPT version 0.1 – Released January, 2021. This initial release of the app cannot account for multiple sequential burns occurring after 2012. It uses the original Stewart et al. (2021) regeneration models and the 2012 version of GNN basal area maps. It was adapted for the web from poscrptR and incorporates only small modifications of the poscrptR code.
-
The original version of the POstfire Spatial Conifer Regeneration Prediction Tool (POSCRPT) was developed by Kristen Shive and Haiganoush Preisler and was conceived of by Hugh Safford. This version lacked a graphical user interface and was composed of R and Python scripts and GIS files. It did not include taxon-specific predictions or postfire scenarios.